ItemPick¶
Introduction¶
The ItemPick module provides an out-of-the-box perception solution for robotic pick-and-place applications. ItemPick targets the detection of flat surfaces on unknown objects for picking with a suction gripper.
In addition, the module offers:
- A dedicated page on the rc_visard Web GUI for easy setup, configuration, testing, and application tuning.
- The definition of regions of interest to select relevant volumes in the scene (see RoiDB).
- A load carrier detection functionality for bin-picking applications (see LoadCarrier), to provide grasps for items inside a bin only.
- The definition of compartments inside a load carrier to provide grasps for specific volumes of the bin only.
- Support for static and robot-mounted cameras and optional integration with the Hand-eye calibration module, to provide grasps in the user-configured external reference frame.
- A quality value associated to each suggested grasp and related to the flatness of the grasping surface.
- Selection of a sorting strategy to sort the returned grasps.
- 3D visualization of the detection results with grasp points and gripper animations in the Web GUI.
Note
In this chapter, cluster and surface are used as synonyms and identify a set of points (or pixels) with defined geometrical properties.
The module is an optional on-board module of the rc_visard and requires a separate ItemPick license to be purchased.
Computation of grasps¶
The ItemPick module offers a service for computing grasps for suction grippers. The gripper is defined by its suction surface length and width.
The ItemPick module identifies flat surfaces in the scene and supports
flexible and/or deformable items. The type of these item_models is
called UNKNOWN since they don’t need to have a standard geometrical shape.
Optionally, the user can also specify the minimum and maximum size of the item.
Optionally, further information can be given to the modules in a grasp computation request:
- The ID of the load carrier which contains the items to be grasped.
- A compartment inside the load carrier where to compute grasps (see Load carrier compartments).
- The ID of the 3D region of interest where to search for the load carriers if a load carrier is set. Otherwise, the ID of the 3D region of interest where to compute grasps.
- Collision detection information: The ID of the gripper to enable collision checking and optionally a pre-grasp offset to define a pre-grasp position. Details on collision checking are given below in CollisionCheck.
A grasp provided by the ItemPick module represents the recommended
pose of the TCP (Tool Center Point) of the suction gripper.
The grasp type is always set to SUCTION.
For ItemPick with an UNKNOWN item model, the computed grasp pose is the center
of the biggest ellipse that can be inscribed in each surface.
The grasp orientation is a right-handed coordinate system and is defined such
that its z axis is normal to the surface pointing inside the object at the grasp position and
its x axis is directed along the maximum elongation of the ellipse. Since the x axis can have two possible directions,
the one that better fits to the preferred TCP orientation (see Setting the preferred orientation of the TCP) is selected. If the run-time parameter allow_any_grasp_z_rotation
is set to true, the x axis will not be forced to be aligned with the maximum elongation of the graspable ellipse, but can have
any rotation around the z axis. In this case, the returned grasp will have the orientation that best fits to the preferred TCP orientation
and is collision free, if collision checking.
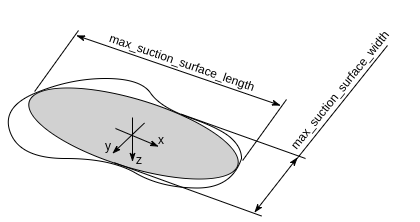
Fig. 32 Illustration of a suction grasp with coordinate system and ellipse representing the maximum suction surface
Each grasp includes the dimensions of the maximum suction surface available,
modelled as an ellipse of axes max_suction_surface_length and
max_suction_surface_width. The user is enabled to filter grasps by specifying
the minimum suction surface required by the suction device in use.
If the run-time parameter allow_any_grasp_z_rotation
is set to true, max_suction_surface_length and
max_suction_surface_width will be equal and correspond to the shortest axis of the largest
graspable ellipse.
Each grasp also includes a quality value, which gives an
indication of the flatness of the grasping surface.
The quality value varies between 0 and 1, where higher numbers correspond to a
flatter reconstructed surface.
The grasp definition is complemented by a uuid (Universally Unique Identifier)
and the timestamp of the oldest image that was used to compute the grasp.
Grasp sorting is performed based on the selected sorting strategy. The following sorting strategies
are available and can be set in the Web GUI
or using the set_sorting_strategies service call:
gravity: highest grasp points along the gravity direction are returned first,surface_area: grasp points with the largest surface area are returned first,direction: grasp points with the shortest distance along a defined directionvectorin a givenpose_frameare returned first.distance_to_point: grasp points with the shortest or farthest (iffarthest_firstis true) distance from apointin a givenpose_frameare returned first.
If no sorting strategy is set or default sorting is chosen in the Web GUI, sorting is done based on a combination of
gravity and surface_area.
Setting the preferred orientation of the TCP¶
The ItemPick module determines the reachability of grasp points based on the preferred orientation of the
TCP. The preferred orientation can be set via the set_preferred_orientation service or on
the ItemPick page in the Web GUI.
The resulting direction of the TCP’s z axis is used to reject grasps which cannot be reached by the gripper.
Furthermore, the preferred orientation is used to select one grasp of several possible symmetries that is best reachable for the robot.
The preferred orientation can be set in the camera coordinate frame or in the external coordinate frame, in case a hand-eye calibration is available. If the preferred orientation is specified in the external coordinate frame and the sensor is robot mounted, the current robot pose has to be given to each object detection call. If no preferred orientation is set, the orientation of the left camera (see Coordinate frames ) will be used as the preferred orientation of the TCP.
Interaction with other modules¶
Internally, the ItemPick module depends on, and interacts with other on-board modules as listed below.
Note
All changes and configuration updates to these modules will affect the performance of the ItemPick module.
Stereo camera and Stereo matching¶
The ItemPick module makes internally use of the following data:
- Rectified images from the Camera module
(
rc_camera); - Disparity, error, and confidence images from the Stereo matching module
(
rc_stereomatching).
All processed images are guaranteed to be captured after the module trigger time.
IO and Projector Control¶
In case the rc_visard is used in conjunction with an external random dot projector and
the IO and Projector Control module (rc_iocontrol),
it is recommended to connect the projector to GPIO Out 1 and set
the stereo-camera module’s acquisition mode to SingleFrameOut1
(see Stereo matching parameters), so that
on each image acquisition trigger an image with and without projector pattern is acquired.
Alternatively, the output mode for the GPIO output in use should be set to ExposureAlternateActive
(see Description of run-time parameters).
In either case,
the Auto Exposure Mode exp_auto_mode should be set to AdaptiveOut1 to optimize the exposure
of both images (see Stereo camera parameters).
Hand-eye calibration¶
In case the camera has been calibrated to a robot, the ItemPick module
can automatically provide poses in the robot coordinate frame.
For the ItemPick node’s Services, the frame of the
output poses can be controlled with the pose_frame argument.
Two different pose_frame values can be chosen:
- Camera frame (
camera). All poses provided by the modules are in the camera frame, and no prior knowledge about the pose of the camera in the environment is required. This means that the configured regions of interest and load carriers move with the camera. It is the user’s responsibility to update the configured poses if the camera frame moves (e.g. with a robot-mounted camera). - External frame (
external). All poses provided by the modules are in the external frame, configured by the user during the hand-eye calibration process. The module relies on the on-board Hand-eye calibration module to retrieve the sensor mounting (static or robot mounted) and the hand-eye transformation. If the mounting is static, no further information is needed. If the sensor is robot-mounted, therobot_poseis required to transform poses to and from theexternalframe.
Note
If no hand-eye calibration is available, all pose_frame values should be set to camera.
All pose_frame values that are not camera or external are rejected.
If the sensor is robot-mounted, the current robot_pose has to be provided depending on the value of pose_frame
and the definition of the sorting direction or sorting point:
- If
pose_frameis set toexternal, providing the robot pose is obligatory. - If the sorting direction is defined in
external, providing the robot pose is obligatory. - If the distance-to-point sorting strategy is defined in
external, providing the robot pose is obligatory. - In all other cases, providing the robot pose is optional.
LoadCarrier¶
The ItemPick module uses the load carrier detection functionality provided by the
LoadCarrier module (rc_load_carrier),
with the run-time parameters specified for this module. However, only one load carrier will be
returned and used in case multiple matching load carriers could be found in the scene. In case multiple
load carriers of the same type are visible, a 3D region of interest should be set to ensure that always the
same load carrier is used for the ItemPick module.
CollisionCheck¶
Collision checking can be easily enabled for
grasp computation of the ItemPick module by passing the ID of the used gripper and
optionally a pre-grasp offset to the
compute_grasps service call. The gripper has to be
defined in the GripperDB module
(see Setting a gripper)
and details about collision checking are given in Collision checking within other modules.
If collision checking is enabled, only grasps which are collision free will be returned. However, the visualization images on the ItemPick page of the Web GUI also show colliding grasp points as black ellipses.
The CollisionCheck module’s run-time parameters affect the collision detection as described in CollisionCheck Parameters.
Parameters¶
ItemPick is represented by the rc_itempick node
in the REST-API and are reached in the Web GUI
under .
The user can explore and configure the rc_itempick module’s run-time parameters, e.g.
for development and testing, using the Web GUI or the REST-API interface.
The user can explore and configure the rc_itempick
module’s run-time parameters, e.g. for development and testing, using the Web GUI or the
REST-API interface.
Parameter overview¶
This module offers the following run-time parameters:
| Name | Type | Min | Max | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
allow_any_grasp_z_rotation |
bool | false | true | false | Whether the grasps are allowed to have arbitrary rotation instead being aligned with the major axis of the graspable ellipse |
cluster_max_curvature |
float64 | 0.005 | 0.5 | 0.11 | Maximum curvature allowed within one cluster. The smaller this value, the more clusters will be split apart. |
cluster_max_dimension |
float64 | 0.05 | 2.0 | 0.3 | Maximum allowed diameter for a cluster in meters. Clusters with a diameter larger than this value are not used for grasp computation. |
clustering_discontinuity_factor |
float64 | 0.1 | 5.0 | 1.0 | Factor used to discriminate depth discontinuities within a patch. The smaller this value, the more clusters will be split apart. |
clustering_max_surface_rmse |
float64 | 0.0005 | 0.01 | 0.004 | Maximum root-mean-square error (RMSE) in meters of points belonging to a surface |
clustering_patch_size |
int32 | 3 | 10 | 4 | Size in pixels of the square patches the depth map is subdivided into during the first clustering step |
grasp_filter_-orientation_threshold |
float64 | 0.0 | 180.0 | 45.0 | Maximum allowed orientation change between grasp and preferred orientation in degrees |
max_grasps |
int32 | 1 | 20 | 5 | Maximum number of provided grasps |
Description of run-time parameters¶
Each run-time parameter is represented by a row on the Web GUI’s ItemPick page. The name in the Web GUI is given in brackets behind the parameter name and the parameters are listed in the order they appear in the Web GUI:
max_grasps (Maximum Grasps)¶
sets the maximum number of provided grasps.
Via the REST-API, this parameter can be set as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters/parameters?max_grasps=<value>PUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters?max_grasps=<value>
cluster_max_dimension (Cluster Maximum Dimension)¶
is the maximum allowed diameter for a cluster in meters. Clusters with a diameter larger than this value are not used for grasp computation.
Via the REST-API, this parameter can be set as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters/parameters?cluster_max_dimension=<value>PUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters?cluster_max_dimension=<value>
cluster_max_curvature (Cluster Maximum Curvature)¶
is the maximum curvature allowed within one cluster. The smaller this value, the more clusters will be split apart.
Via the REST-API, this parameter can be set as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters/parameters?cluster_max_curvature=<value>PUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters?cluster_max_curvature=<value>
clustering_patch_size (Patch Size)¶
is the size of the square patches the depth map is subdivided into during the first clustering step in pixels.
Via the REST-API, this parameter can be set as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters/parameters?clustering_patch_size=<value>PUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters?clustering_patch_size=<value>
clustering_discontinuity_factor (Discontinuity Factor)¶
is the factor used to discriminate depth discontinuities within a patch. The smaller this value, the more clusters will be split apart.
Via the REST-API, this parameter can be set as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters/parameters?clustering_discontinuity_factor=<value>PUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters?clustering_discontinuity_factor=<value>
clustering_max_surface_rmse (Maximum Surface RMSE)¶
is the maximum root-mean-square error (RMSE) in meters of points belonging to a surface.
Via the REST-API, this parameter can be set as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters/parameters?clustering_max_surface_rmse=<value>PUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters?clustering_max_surface_rmse=<value>
grasp_filter_orientation_threshold (Grasp Orientation Threshold)¶
is the maximum deviation of the TCP’s z axis at the grasp point from the z axis of the TCP’s preferred orientation in degrees. Only grasp points which are within this threshold are returned. When set to zero, any deviations are valid.
Via the REST-API, this parameter can be set as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/<0,1,2,3>/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters?grasp_filter_orientation_threshold=<value>PUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters?grasp_filter_orientation_threshold=<value>
allow_any_grasp_z_rotation (Allow Any Grasp Z Rotation)¶
If set to true, the returned grasps are no longer forced to have their x axes aligned with the maximum elongation of the graspable ellipse, but can have any rotation around the z axis. The returned
max_suction_surface_lengthandmax_suction_surface_widthwill be equal and correspond to the shortest diameter of the largest graspable ellipse. This parameter enables the robot to get more options for grasping objects, especially in scenes where collisions can occur. However, in case ofUNKNOWNitem models, since the grasp is no longer aligned with the graspable ellipse, the correct orientation for placing the object must be determined by other means.Via the REST-API, this parameter can be set as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/<0,1,2,3>/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters?allow_any_grasp_z_rotation=<value>PUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/parameters?allow_any_grasp_z_rotation=<value>
Status values¶
The rc_itempick node reports the following status values:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
data_acquisition_time |
Time in seconds required by the last active service to acquire images |
grasp_computation_time |
Processing time of the last grasp computation in seconds |
last_timestamp_processed |
The timestamp of the last processed dataset |
load_carrier_detection_time |
Processing time of the last load carrier detection in seconds |
processing_time |
Processing time of the last detection (including load carrier detection) in seconds |
state |
The current state of the rc_itempick node |
The reported state can take one of the following values.
| State name | Description |
|---|---|
| IDLE | The module is idle. |
| RUNNING | The module is running and ready for load carrier detection and grasp computation. |
| FATAL | A fatal error has occurred. |
Services¶
The user can explore and call the rc_itempick node’s services,
e.g. for development and testing, using the
REST-API interface or
the rc_visard
Web GUI.
The ItemPick module offers the following services.
compute_grasps¶
Triggers the computation of grasping poses for a suction device as described in Computation of grasps.
Details
This service can be called as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/services/compute_graspsPUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/services/compute_graspsRequired arguments:
pose_frame: see Hand-eye calibration.
suction_surface_length: length of the suction device grasping surface.
suction_surface_width: width of the suction device grasping surface.Potentially required arguments:
robot_pose: see Hand-eye calibration.Optional arguments:
load_carrier_id: ID of the load carrier which contains the items to be grasped.
load_carrier_compartment: compartment inside the load carrier where to compute grasps (see Load carrier compartments).
region_of_interest_id: ifload_carrier_idis set, ID of the 3D region of interest where to search for the load carriers. Otherwise, ID of the 3D region of interest where to compute grasps.
item_models: list of items to be detected. In case of ItemPick, currently only a single item model of typeUNKNOWNwith minimum and maximum dimensions is supported, with the minimum dimensions strictly smaller than the maximum dimensions.
collision_detection: see Collision checking within other modules.The definition for the request arguments with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "args": { "collision_detection": { "gripper_id": "string", "pre_grasp_offset": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" } }, "item_models": [ { "type": "string", "unknown": { "max_dimensions": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "min_dimensions": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" } } } ], "load_carrier_compartment": { "box": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "pose": { "orientation": { "w": "float64", "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "position": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" } } }, "load_carrier_id": "string", "pose_frame": "string", "region_of_interest_id": "string", "robot_pose": { "orientation": { "w": "float64", "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "position": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" } }, "suction_surface_length": "float64", "suction_surface_width": "float64" } }
load_carriers: list of detected load carriers.
grasps: sorted list of suction grasps.
items: sorted list of items corresponding to the returned grasps. In case of ItemPick, this list is always empty.
timestamp: timestamp of the image set the detection ran on.
return_code: holds possible warnings or error codes and messages.The definition for the response with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "name": "compute_grasps", "response": { "grasps": [ { "item_uuid": "string", "max_suction_surface_length": "float64", "max_suction_surface_width": "float64", "pose": { "orientation": { "w": "float64", "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "position": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" } }, "pose_frame": "string", "quality": "float64", "timestamp": { "nsec": "int32", "sec": "int32" }, "type": "string", "uuid": "string" } ], "items": [ { "bounding_box": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "grasp_uuids": [ "string" ], "pose": { "orientation": { "w": "float64", "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "position": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" } }, "pose_frame": "string", "template_id": "string", "timestamp": { "nsec": "int32", "sec": "int32" }, "type": "string", "uuid": "string", "view_name": "string", "view_pose_set": "bool", "view_uuid": "string" } ], "load_carriers": [ { "height_open_side": "float64", "id": "string", "inner_dimensions": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "outer_dimensions": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "overfilled": "bool", "pose": { "orientation": { "w": "float64", "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "position": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" } }, "pose_frame": "string", "rim_ledge": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64" }, "rim_step_height": "float64", "rim_thickness": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64" }, "type": "string" } ], "return_code": { "message": "string", "value": "int16" }, "timestamp": { "nsec": "int32", "sec": "int32" } } }
set_preferred_orientation¶
Persistently stores the preferred orientation of the TCP to compute the reachability of the grasps, which is used for filtering and the grasps returned by the
compute_graspsservice (see Setting the preferred orientation of the TCP).Details
This service can be called as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/services/set_preferred_orientationPUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/services/set_preferred_orientationThe definition for the request arguments with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "args": { "orientation": { "w": "float64", "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "pose_frame": "string" } }The definition for the response with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "name": "set_preferred_orientation", "response": { "return_code": { "message": "string", "value": "int16" } } }
get_preferred_orientation¶
Returns the preferred orientation of the TCP to compute the reachability of the grasps, which is used for filtering the grasps returned by the
compute_graspsservice (see Setting the preferred orientation of the TCP).Details
This service can be called as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/services/get_preferred_orientationPUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/services/get_preferred_orientationThis service has no arguments.The definition for the response with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "name": "get_preferred_orientation", "response": { "orientation": { "w": "float64", "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "pose_frame": "string", "return_code": { "message": "string", "value": "int16" } } }
set_sorting_strategies¶
Persistently stores the sorting strategy for sorting the grasps returned by the
compute_graspsservice (see Computation of grasps).Details
This service can be called as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/services/set_sorting_strategiesPUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/services/set_sorting_strategiesOnly one strategy may have a
weightgreater than 0. If allweightvalues are set to 0, the module will use the default sorting strategy.If the weight for
directionis set, thevectormust contain the direction vector andpose_framemust be eithercameraorexternal.If the weight for
distance_to_pointis set,pointmust contain the sorting point andpose_framemust be eithercameraorexternal.The definition for the request arguments with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "args": { "direction": { "pose_frame": "string", "vector": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "weight": "float64" }, "distance_to_point": { "farthest_first": "bool", "point": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "pose_frame": "string", "weight": "float64" }, "gravity": { "weight": "float64" }, "surface_area": { "weight": "float64" } } }The definition for the response with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "name": "set_sorting_strategies", "response": { "return_code": { "message": "string", "value": "int16" } } }
get_sorting_strategies¶
Returns the sorting strategy for sorting the grasps returned by the
compute-graspsservice (see Computation of grasps).Details
This service can be called as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/services/get_sorting_strategiesPUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/services/get_sorting_strategiesThis service has no arguments.All
weightvalues are 0 when the module uses the default sorting strategy.The definition for the response with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "name": "get_sorting_strategies", "response": { "direction": { "pose_frame": "string", "vector": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "weight": "float64" }, "distance_to_point": { "farthest_first": "bool", "point": { "x": "float64", "y": "float64", "z": "float64" }, "pose_frame": "string", "weight": "float64" }, "gravity": { "weight": "float64" }, "return_code": { "message": "string", "value": "int16" }, "surface_area": { "weight": "float64" } } }
start¶
Starts the module. If the command is accepted, the module moves to state
RUNNING.Details
This service can be called as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/services/startPUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/services/startThis service has no arguments.The
current_statevalue in the service response may differ fromRUNNINGif the state transition is still in process when the service returns.The definition for the response with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "name": "start", "response": { "accepted": "bool", "current_state": "string" } }
stop¶
Stops the module. If the command is accepted, the module moves to state
IDLE.Details
This service can be called as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/services/stopPUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/services/stopThis service has no arguments.The
current_statevalue in the service response may differ fromIDLEif the state transition is still in process when the service returns.The definition for the response with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "name": "stop", "response": { "accepted": "bool", "current_state": "string" } }
reset_defaults¶
Resets all parameters of the module to its default values, as listed in above table. Also resets sorting strategies.
Details
This service can be called as follows.
PUT http://<host>/api/v2/pipelines/0/nodes/rc_itempick/services/reset_defaultsPUT http://<host>/api/v1/nodes/rc_itempick/services/reset_defaultsThis service has no arguments.The definition for the response with corresponding datatypes is:
{ "name": "reset_defaults", "response": { "return_code": { "message": "string", "value": "int16" } } }
Return codes¶
Each service response contains a return_code,
which consists of a value plus an optional message.
A successful service returns with a return_code value of 0.
Negative return_code values indicate that the service failed.
Positive return_code values indicate that the service succeeded with additional information.
The smaller value is selected in case a service has multiple return_code values,
but all messages are appended in the return_code message.
The following table contains a list of common codes:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Success |
| -1 | An invalid argument was provided |
| -3 | An internal timeout occurred, e.g. during box detection if the given dimension range is too large |
| -4 | Data acquisition took longer than allowed |
| -8 | The template has been deleted during detection. |
| -10 | New element could not be added as the maximum storage capacity of load carriers, regions of interest or template has been exceeded |
| -11 | Sensor not connected, not supported or not ready |
| -200 | Fatal internal error |
| -301 | More than one item model provided to the compute_grasps service |
| 10 | The maximum storage capacity of load carriers, regions of interest or templates has been reached |
| 11 | An existent persistent model was overwritten by the call to set_load_carrier or set_region_of_interest |
| 100 | The requested load carriers were not detected in the scene |
| 101 | No valid surfaces or grasps were found in the scene |
| 102 | The detected load carrier is empty |
| 103 | All computed grasps are in collision with the load carrier |
| 112 | Rejected detections of one or more clusters, because min_cluster_coverage was not reached. |
| 300 | A valid robot_pose was provided as argument but it is not required |
| 999 | Additional hints for application development |